Submitted by NFU
On the Canadian Prairies, small and medium-sized family farms are often portrayed as the primary food production units. Yet, the reality of farming in Western Canada is quite different. In fact, a small and declining number of farms are operating the lion’s share of Prairie farmland and capturing the lion’s share of farm revenue and net income.��
��
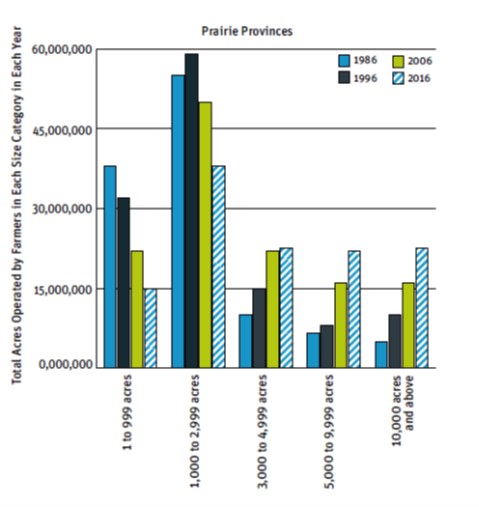
Concentration Matters: Farmland Inequality on the Prairies��by Darrin Qualman, Annette Aurélie Desmarais, André Magnan and Mengistu Wendimu demonstrates that the ownership and control of Canada’s food-producing land is becoming more and more concentrated, with profound impacts for young farmers, food system security, climate change and democracy.
The authors analyse the extent of farmland concentration in Canada’s three Prairie provinces (Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba), where over 70 percent of the country’s agricultural land is situated. They find that 38 percent of Saskatchewan’s farmland is operated and controlled by just 8 percent of farms. In Alberta, 6 percent of farms operate 40 percent of that province’s farmland, while Manitoba sees 4 percent of farms operate and control 24 percent of the land. Co-author Annette Aurélie Desmarais – Canada Research Chair at the University of Manitoba – observes that such concentration makes it much harder for young and new farmers to enter agriculture, “The number of young farmers in Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba has declined by more than 70 percent. An astonishing amount within just one generation.”
The persistent decline in the number of farmers, farm size expansion, growing farm income inequality, and increased land concentration have other effects as well. Co-author and University of Regina professor André Magnan argues that rural economies, communities, businesses, and services are also affected as there are “fewer farm families to patronize local shops and services, while farmers lose their capacity to democratically influence governments and legislation as their voting numbers fall. Meanwhile, non-farmers lose their connections to farms and rural culture as fewer and fewer urban residents count farmers among their family members or friends.” A series of policy measures are urgently needed to counter the market forces that will otherwise drive us toward even more concentrated farmland ownership and “drive half of Canadian farm families off the land in the next one to two generations.”
View the full report:��
��